Andrew White | FutureHouse
Automating Scientific Discovery
Andrew White
FutureHouse
August 2025
FutureHouse Structure
- Non-profit founded in 2023
- Funded primarily by Eric Schmidt
- Based in San Francisco
- 25 employees
Science is changing independent of AI
Arxiv.org,10.6084/m9.figshare.17064419.v3
Intellectual bottlenecks are growing
📝 Increasing paper count ($\approx$5M per year)
🧬 Larger data sets from cheaper
experiments (genome at
$200 per person, $1 / GB of sequencing)
🔍95% decline in disruptive papers since 1980
Park, M. et al. Nature 613, 138-144 (2023); Scannell, J.W. et al. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 11, 191–200 (2012); Deloitte 2025: Pharma innovation returns.
FutureHouse Mission
Accelerate Scientific Discovery
What is an agent?
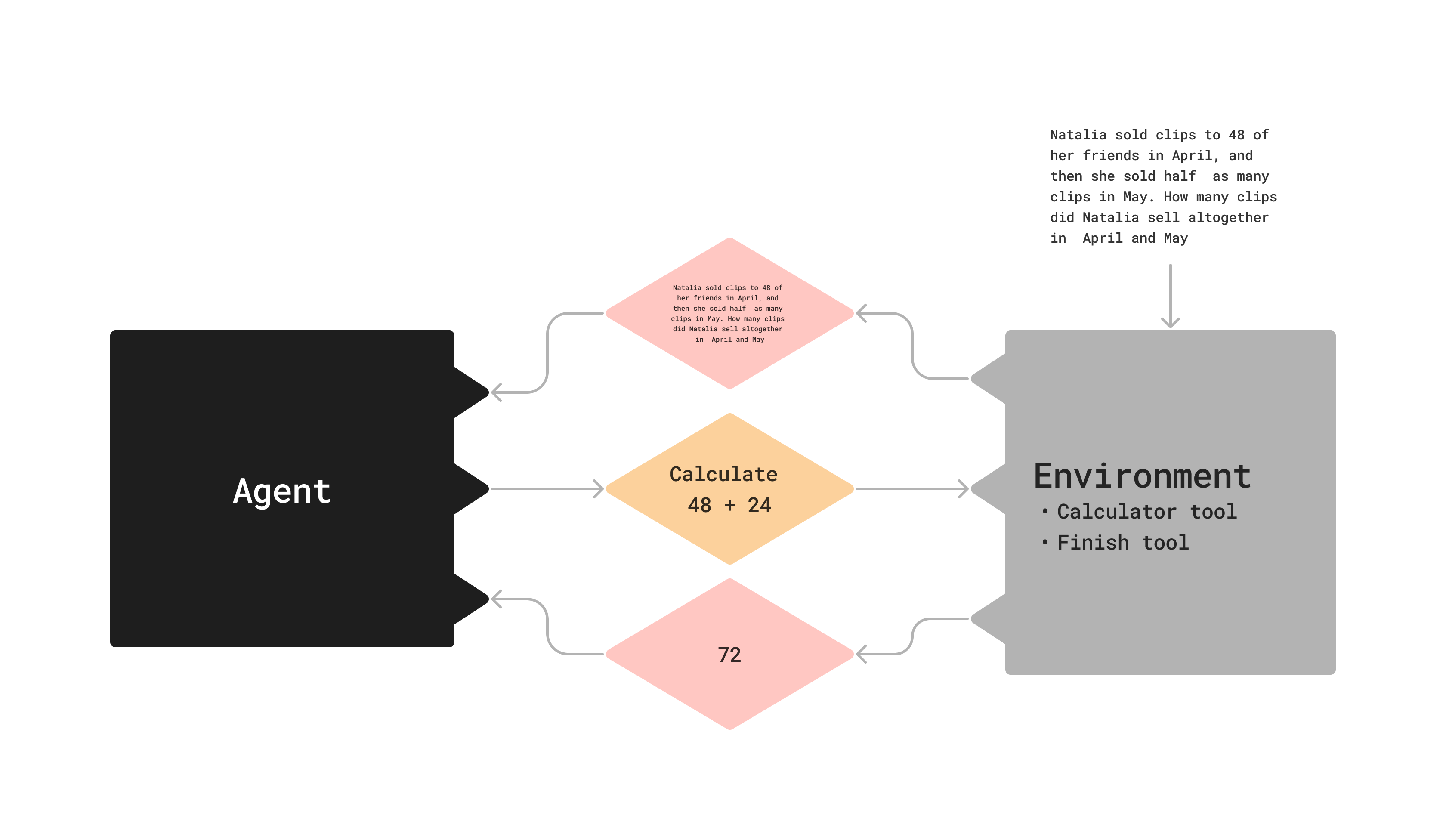
Agent: trained, makes decisions
Environment: untrained, has tools, state
Protein Design Environment
- Protein design with 5 existing deep learning models
- Molecular dynamics, bioinformatics, literature research agent
- Input: "design 92 binders for PD-L1"
Wet lab validation
Aviary Code
First message to agent
Aviary Code
Create tools

Aviary Code
Use environment

Learning vs Frontier Models
Crows
| Environment | Key Tools | |
|---|---|---|
| Crow/Falcon | Literature Research | Search, Citation Traversal |
| ProteinCrow | Designing novel proteins | AlphaFold2, Molecular Dynamics |
| ChemCrow/Phoenix | Designing new molecules | Retrosynthesis, self-driving robotic lab |
| Data analysis crow | Generating discoveries from data | bioinformatics tools, code, file system |
Agent vs ML Model
Modify surface residues of IL-10 to increase expression and solubility in E. coli without disrupting dimerization or receptor interaction.
Automating research of scientific literature
Language agents achieve superhuman synthesis of scientific knowledge
Michael D. Skarlinski, Sam Cox, Jon M. Laurent, James D. Braza, Michaela Hinks, Michael J. Hammerling, Manvitha Ponnapati, Samuel G. Rodriques, Andrew D. White arXiv:2409.13740, 2024
Better at answering questions than PhD biology experts
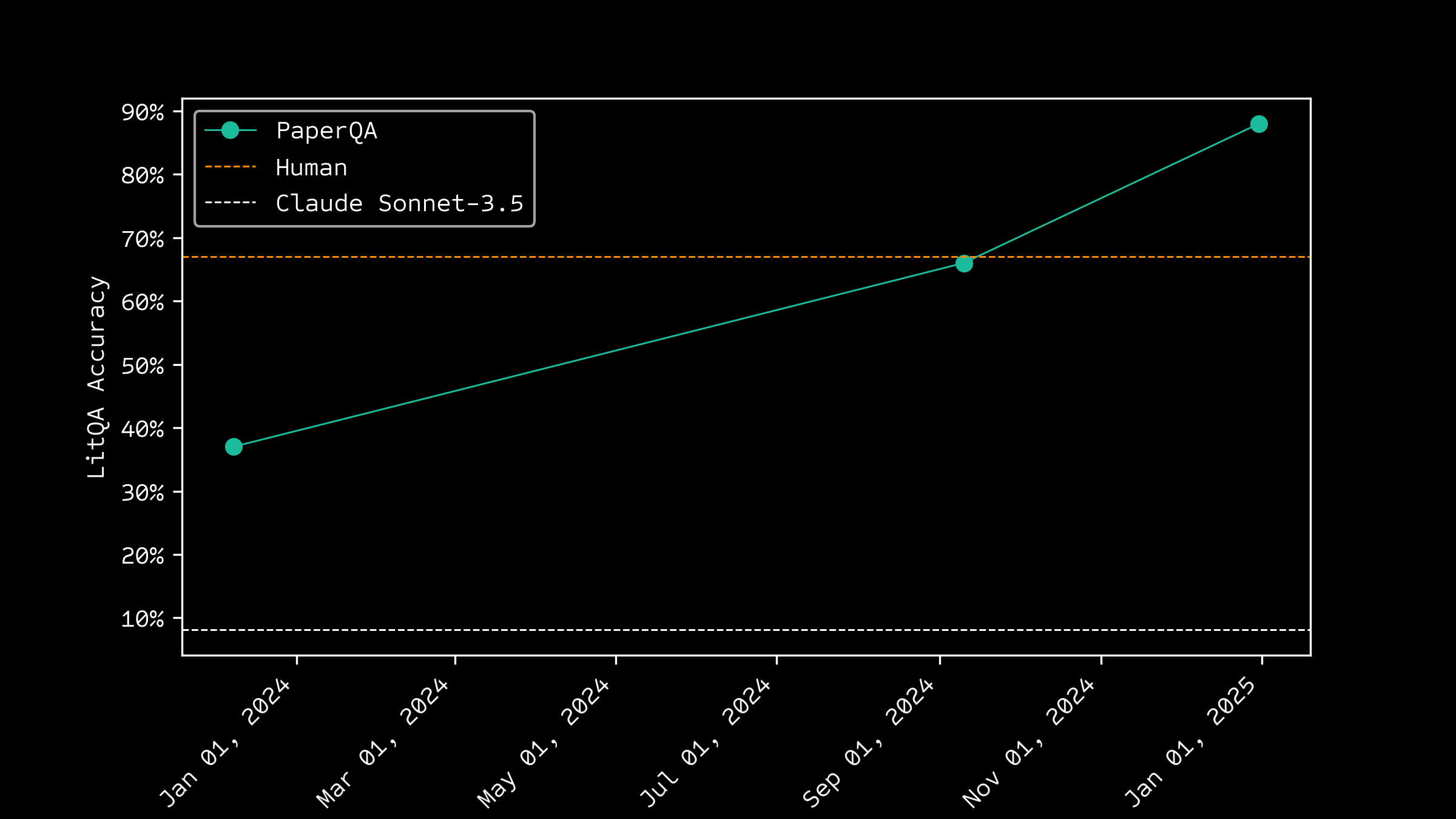
Improving over time
Better than human written Wikipedia articles
FutureHouse Platform
- Free, with rate limits
- API - can be incorporated into your pipeline/agents
- Majority of code is open source
API
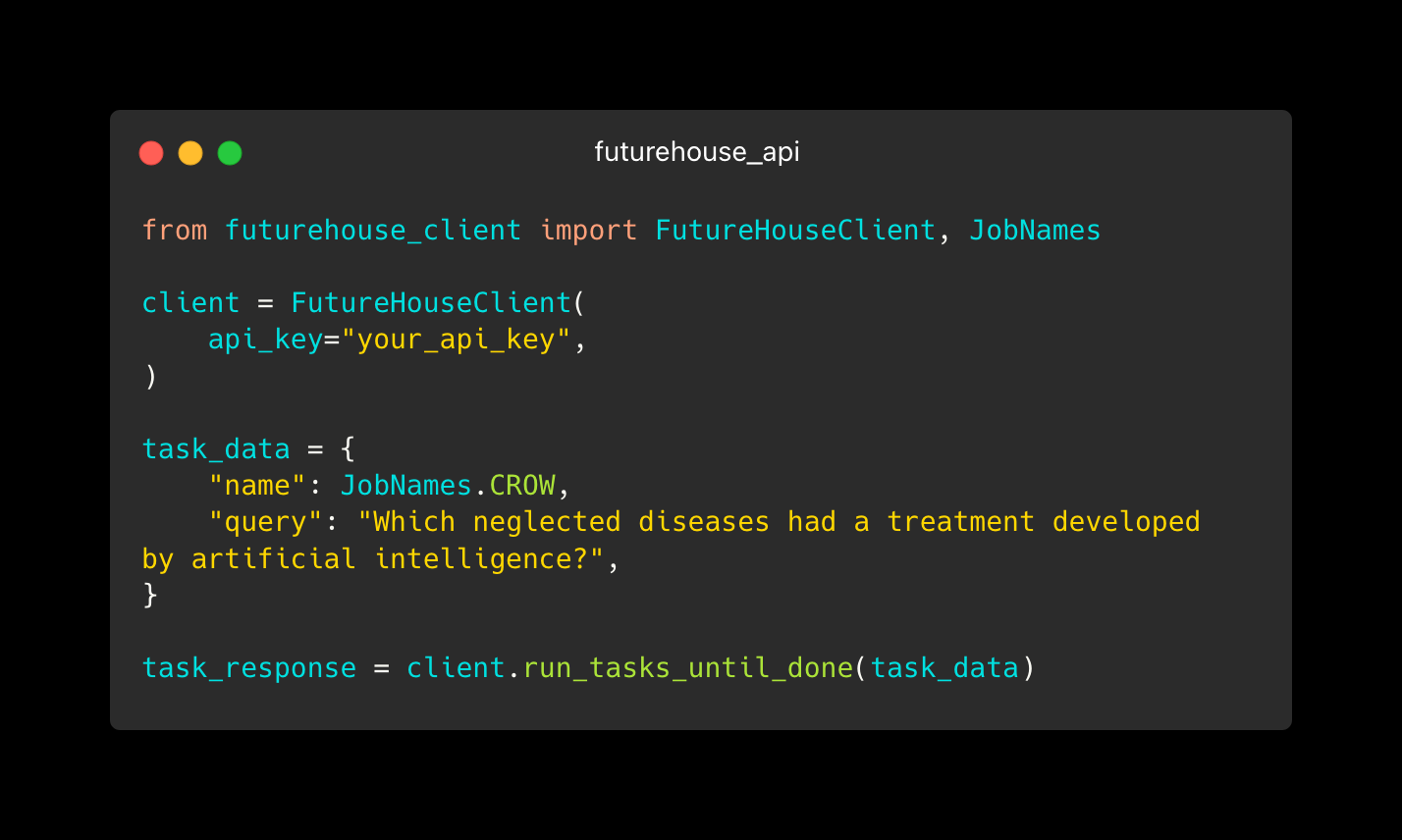
- Tasks per minute: 150
- Research Papers 100,000,000
- Wiki page for all diseases every 14 hours
- All arxiv papers per week 25,000 papers / month
- Check for contradictions 6.3M papers / year
- All Wikipedia every 6 weeks
Model intelligence will continue to increase
Complete cycle of disease to mechanism to target to drug
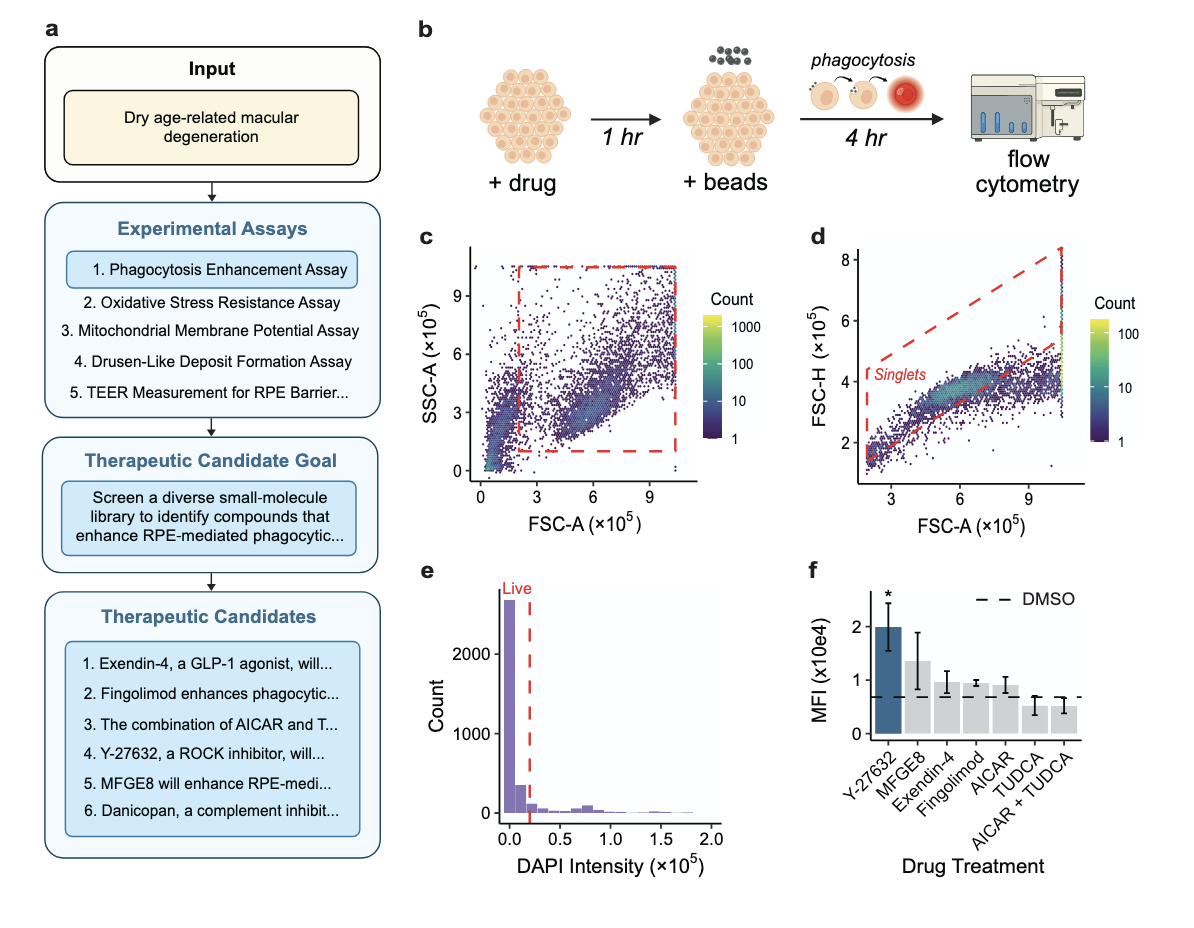
ROBIN: A Multi-Agent System for Automating Scientific Discovery
Ali Essam Ghareeb*, Benjamin Chang*, Ludovico Mitchener, Angela Yiu, Caralyn J. Szostkiewicz, Jon M. Laurent, Muhammed T. Razzak, Andrew D. White†, Michaela M. Hinks‡, Samuel G. Rodriques
Scientific Reasoning Models
Training a Scientific Reasoning Model for Chemistry
Siddharth M. Narayanan, James D. Braza, Ryan-Rhys Griffiths, Albert Bou, Geemi Wellawatte, Mayk Caldas Ramos, Ludovico Mitchener, Samuel G. Rodriques, Andrew D. White arXiv:2506.17238, 2025
Improving Models
| Pretraining | Large Data, Large Compute |
| Scaffolding | Domain knowledge |
| Reasoning | Domain knowledge, small data, small compute |
Reasoning scaling
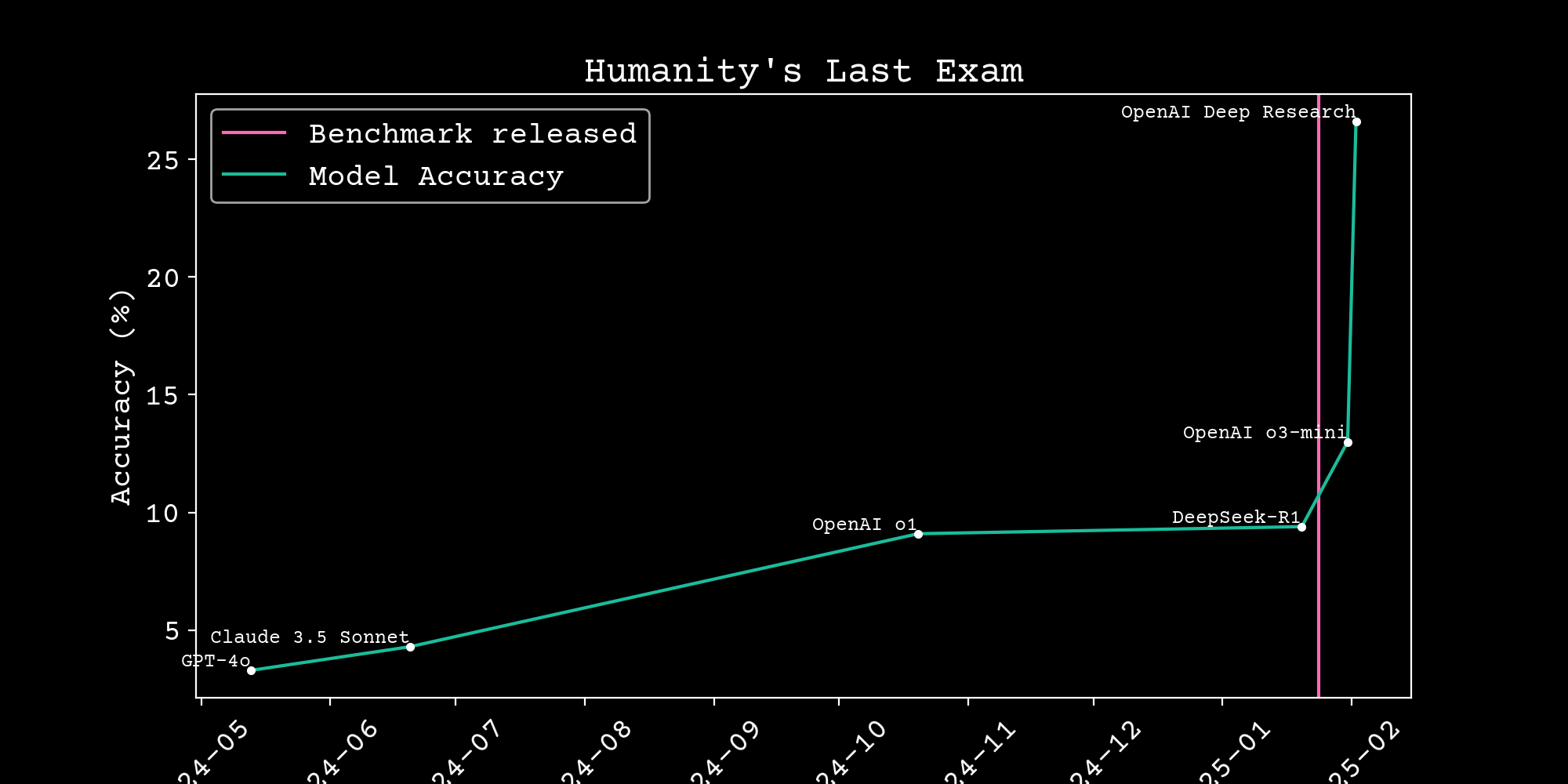
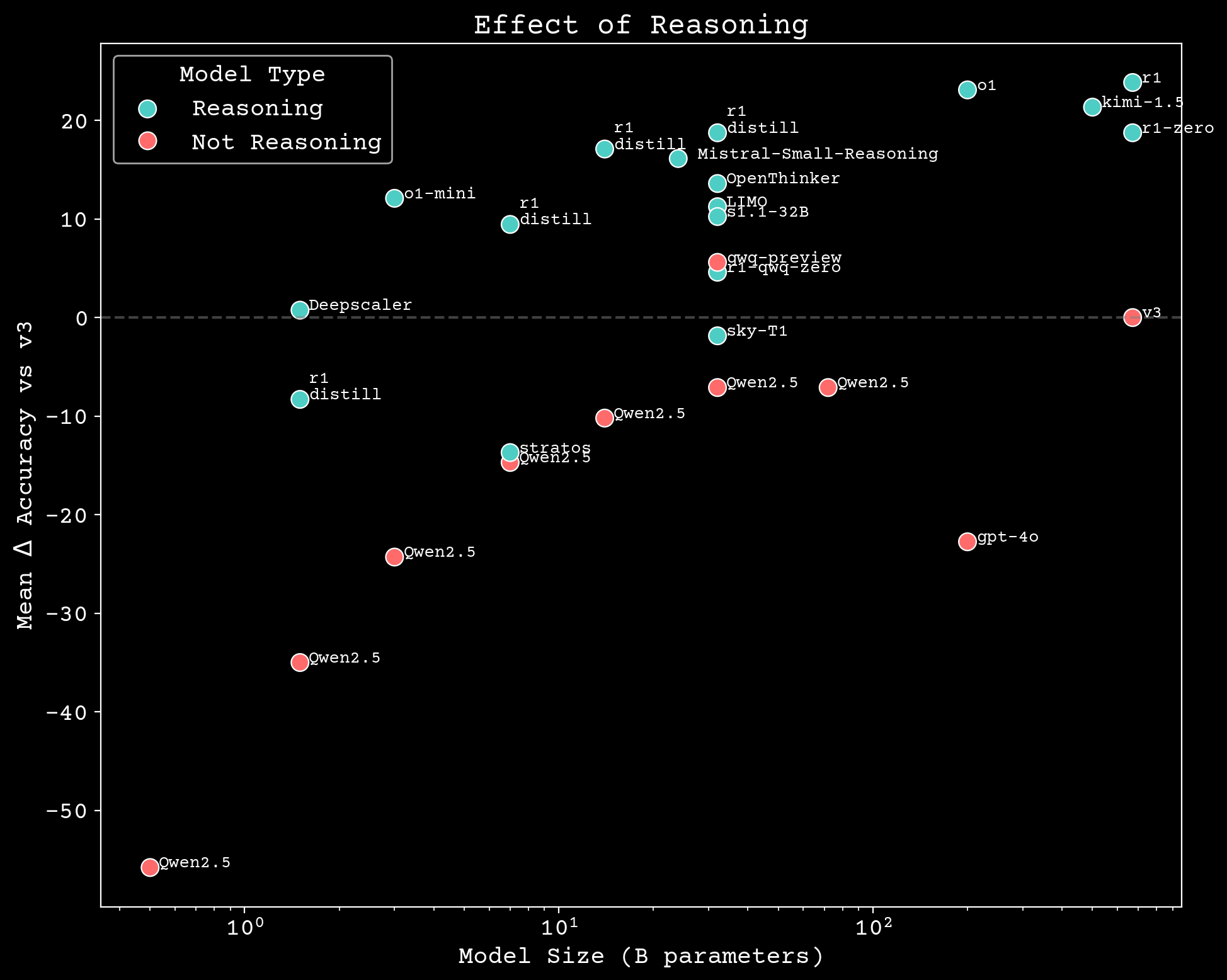
Can we build scientific reasoning models?
chemistry reasoning model
Works with molecular structures, but reasons in English
Start from base LLM and teach it chemistry
What can a reasoning model do?
Q:Propose a 1-step synthesis path that uses only commercially available reagents
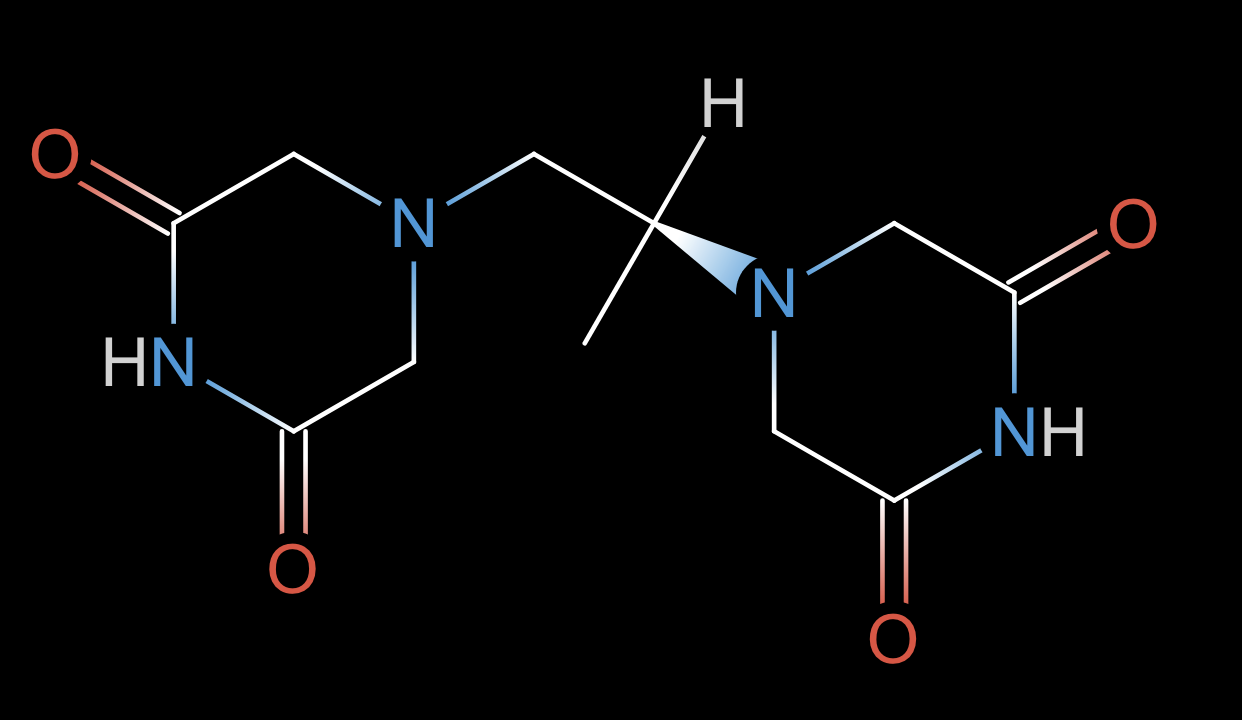
Q: Propose a modification to this molecule to increase its solubility by about 1 LogS unit without affecting its scaffold.
data
| Task | Subtasks | Examples | Verifier | Templates | Data source name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| functional group | 1 | 74562 | code | 6 | ChEMBL |
| organism molecular formula | 1 | 74164 | molecule comparison | 10 | COCONUT |
| IUPAC name | 1 | 74994 | code | 10 | COCONUT |
| SMILES completion | 1 | 74990 | code | 10 | COCONUT |
| solubility edit | 3 | 115977 | ML model, code | 15 | ChEMBL |
| scent | 180 | 4240 | multiple choice | 8 | pyFUME |
| reaction prediction | 1 | 61205 | molecule comparison | 10 | ORD |
| retrosynthesis | 1 | 67252 | ML model, database | 8 | mcule |
| BBB permeability | 2 | 2064 | multiple choice | 8 | BBB |
| pKa | 4 | 336 | multiple choice | 8 | IUPAC |
| safety | 11 | 5687 | multiple choice | 8 | Pubchem |
| molecular formula | 1 | 18738 | code | 10 | COCONUT |
| ADME | 12 | 1030 | multiple choice | 8 | Fang ADME |
| LD50 | 2 | 342 | multiple choice | 8 | Pubchem |
| Human receptor binding | 150 | 1663 | multiple choice | 8 | EveBio |
| property-regression-solubility | 2 | 464 | multiple choice | 8 | AqSolDB |
| property-regression-photo | 1 | 23 | multiple choice | 8 | Photoswitches |
| Total | 374 | 577790 | 8 | 81* | 12 |
Training Stages
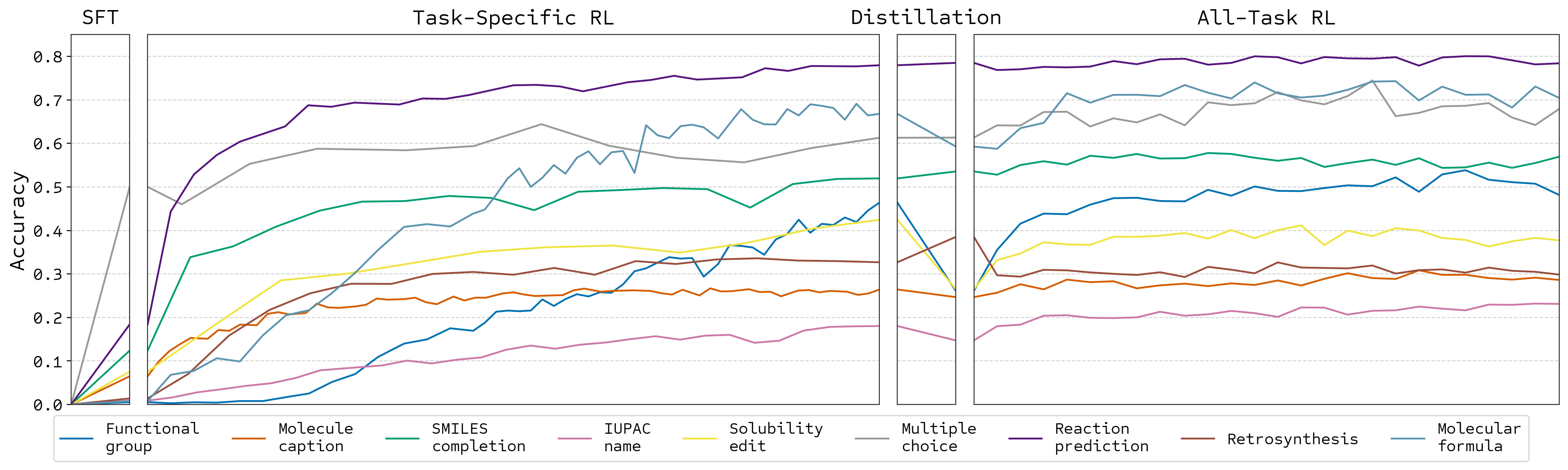
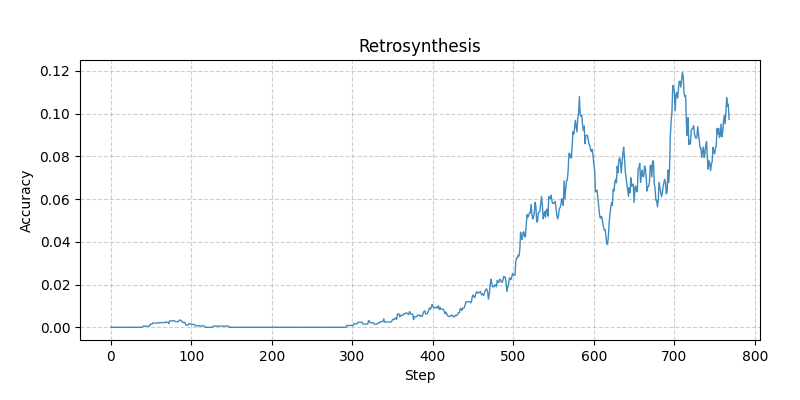
Can learn from zero accuracy
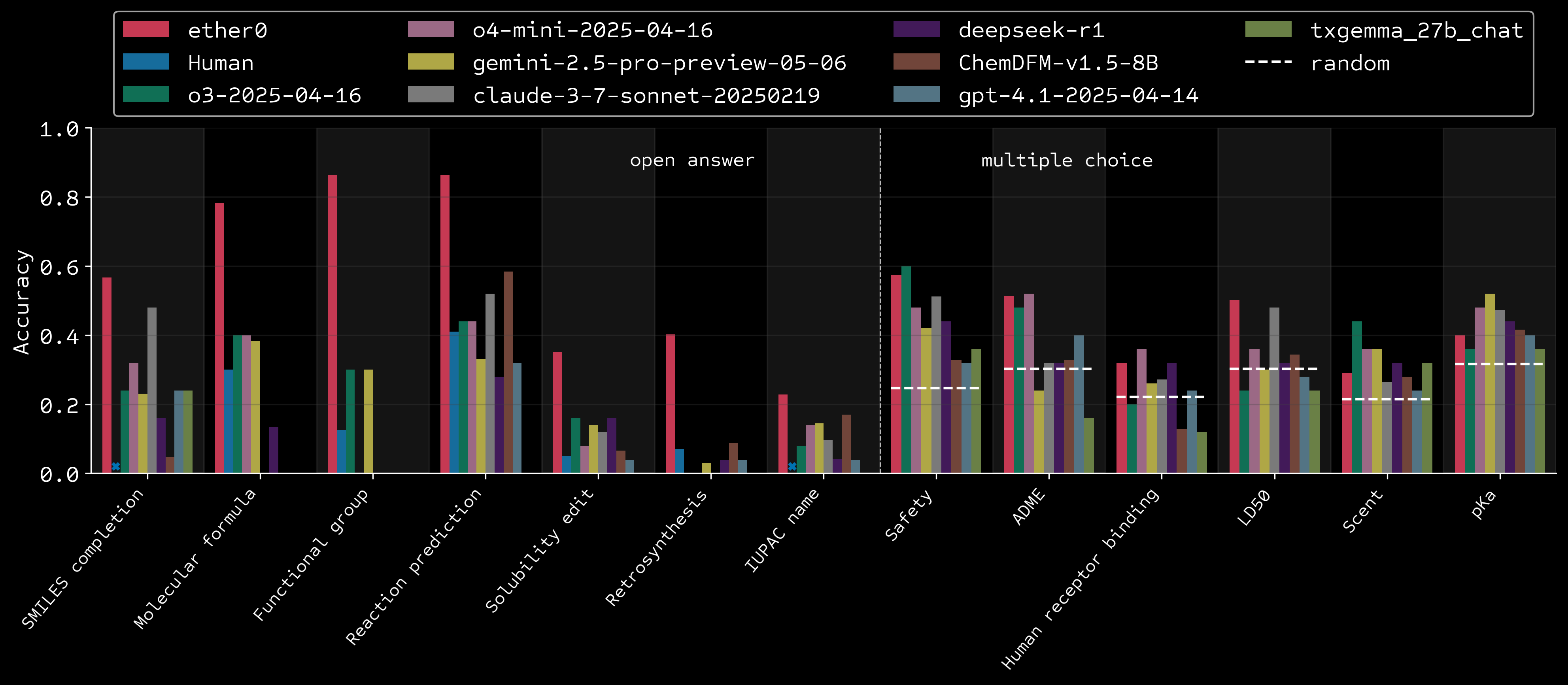
Results vs humans and frontier models
Reasoning behavior
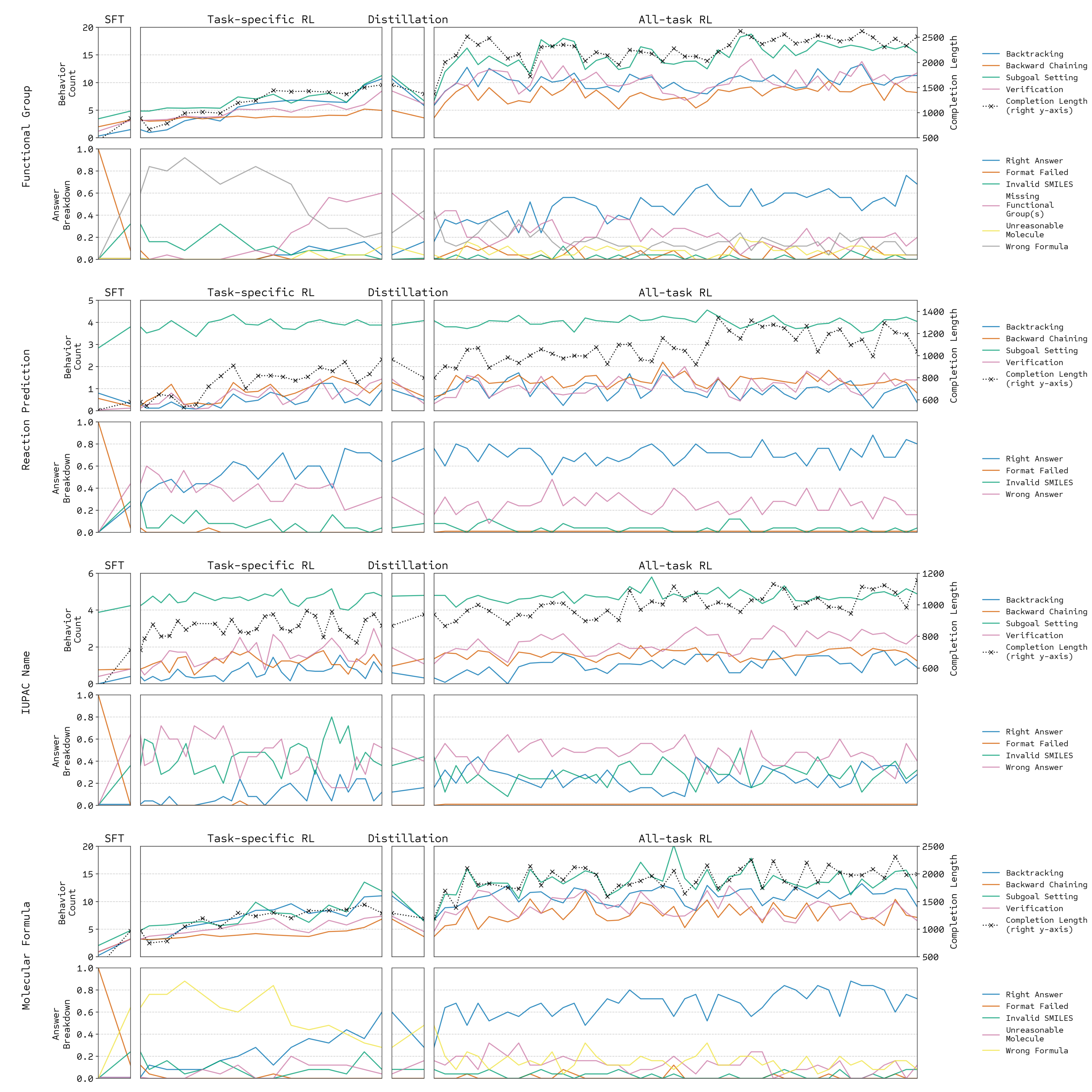
Ablation
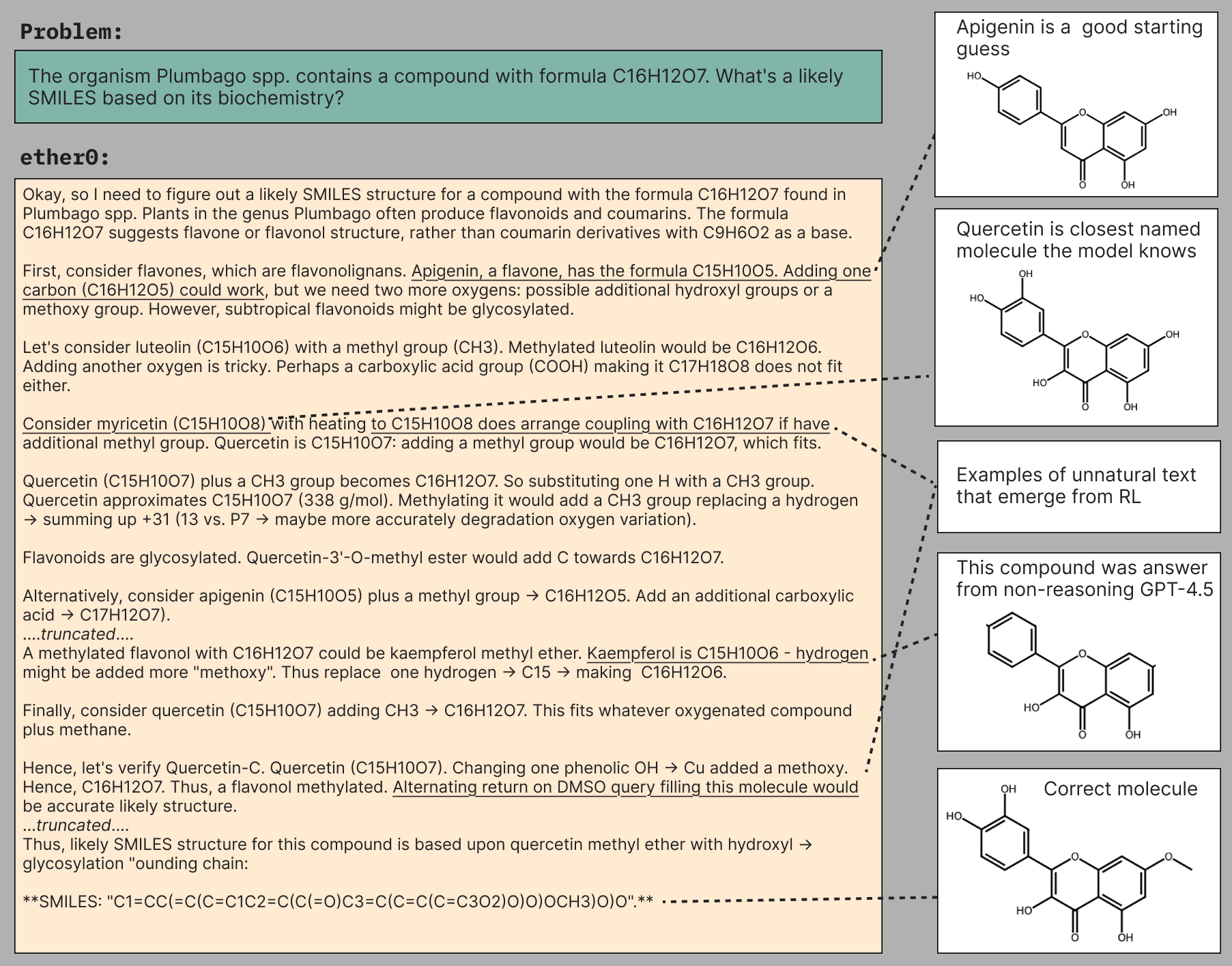
More data efficient
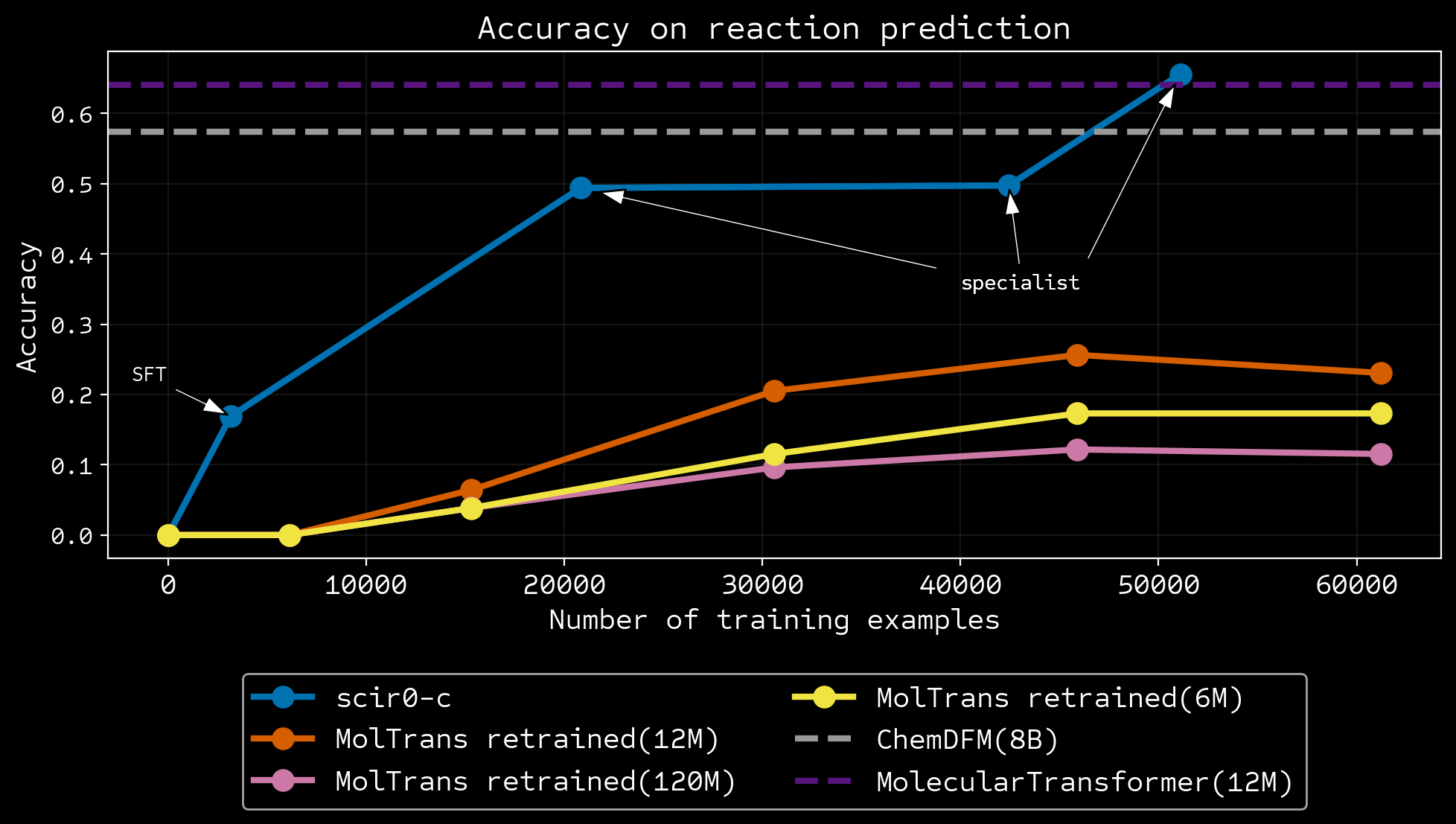
Ablation